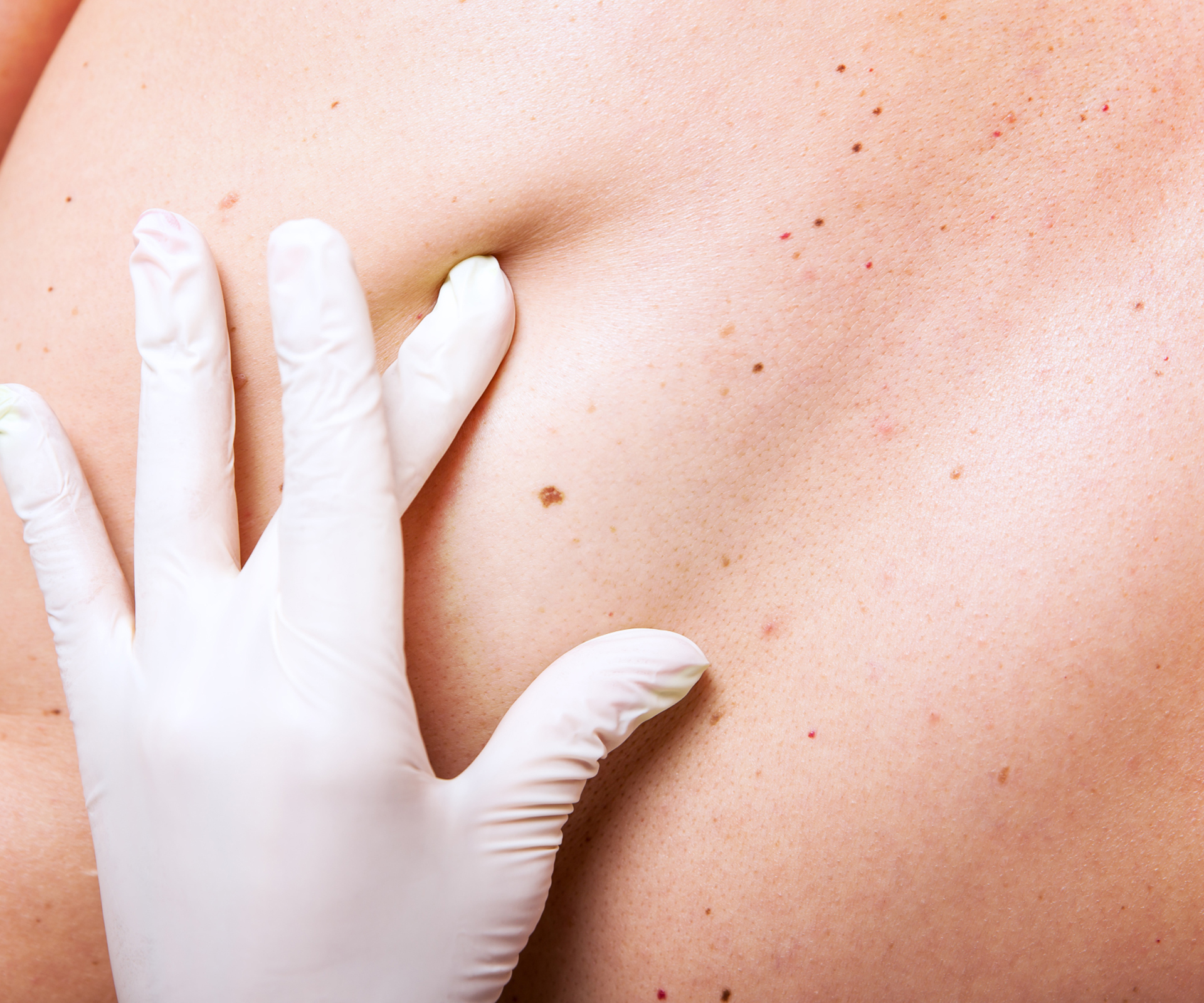
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the skin grow uncontrollably. There are three main types of skin cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This is the most common type of skin cancer. It typically appears as a small, shiny bump or a sore that doesn’t heal. BCC usually develops on areas of the skin exposed to the sun.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): SCC often looks like a scaly, red patch or a sore that bleeds. It is more likely to spread than BCC but is still highly treatable if caught early.
- Melanoma: This is the most serious type of skin cancer. Melanoma usually starts as a mole or pigmented area that changes in size, shape, or color. It can spread to other parts of the body if not treated early.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing skin cancer:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can damage skin cells, increasing the risk of skin cancer. People who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper protection are at higher risk.
- Tanning Beds: Artificial UV radiation from tanning beds can also cause skin damage and increase cancer risk.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer because their skin has less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer can increase your risk, as some genetic factors may predispose individuals to the disease.
- Previous Skin Cancer: If you have had skin cancer before, you are at higher risk of developing it again.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, although it can affect people of all ages.
Symptoms and Signs
Knowing what to look for can help with early detection. Common signs and symptoms of skin cancer include:
- Changes in Moles or Spots: Any change in the size, shape, or color of a mole or spot should be checked by a doctor.
- New Growths: A new growth or sore that does not heal may be a sign of skin cancer.
- Itching or Tenderness: Areas of the skin that itch or are tender, especially if they have changed in appearance, should be examined.
- Bleeding or Oozing: Any area of the skin that bleeds, oozes, or crusts over may indicate skin cancer.
Prevention Tips
Preventing skin cancer involves protecting your skin from UV radiation and adopting healthy habits:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every two hours, especially when spending time outdoors.
- Seek Shade: Avoid direct sunlight, particularly between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are strongest.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-protective sunglasses can help shield your skin from the sun.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Steer clear of tanning beds and artificial UV sources, which can increase skin cancer risk.
- Regular Skin Checks: Perform self-exams to monitor your skin for any changes. Schedule regular check-ups with a dermatologist for professional evaluations.
![]()
Diagnosis and Treatment
If skin cancer is suspected, a dermatologist will perform a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options vary based on the type and stage of skin cancer:
- Surgery: The most common treatment for skin cancer involves removing the cancerous tissue. Procedures can range from minor excisions to more extensive surgeries.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It is often used for non-surgical candidates or for cancers in areas difficult to surgically access.
- Topical Medications: For some non-melanoma skin cancers, topical chemotherapy creams or immune response modifiers can be applied to the affected area.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen, which can be effective for superficial skin cancers.
- Photodynamic Therapy: This treatment uses light-sensitive drugs and a special light to destroy cancer cells. It is used for superficial skin cancers and precancerous conditions.
Living with Skin Cancer
Receiving a skin cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but many people successfully manage the disease and maintain a good quality of life. Follow-up care is essential to monitor for any recurrence or new cancers. Emotional support from loved ones and professional counseling can also be beneficial in coping with the impact of skin cancer.
Skin cancer is a serious but highly treatable condition, especially when detected early. Understanding the risk factors, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk. Regular skin checks and healthy sun habits play a crucial role in skin cancer prevention and early detection.
By staying informed and proactive, you can take charge of your skin health and reduce the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Remember, early action is key to successful treatment and maintaining your overall well-being.