In this article, we’ll explore how different sleeping positions affect your health and provide insights into optimizing your posture for better rest and wellness.
The Importance of Sleeping Position

Your sleeping position can influence various aspects of your health, including spinal alignment, circulation, breathing, and digestion. It can also exacerbate or alleviate chronic pain, snoring, and conditions such as acid reflux or sleep apnea. Since we spend about a third of our lives sleeping, the long-term effects of poor sleeping posture can add up, leading to discomfort and health complications.
Understanding your sleeping position is the first step toward making adjustments that can improve your quality of life.
Common Sleeping Positions and Their Health Impacts

1. Back Sleeping (Supine Position)
Sleeping on your back is often considered one of the healthiest positions because it allows your head, neck, and spine to rest in a neutral position. This alignment reduces the risk of developing back and neck pain.
Benefits:
- Spinal Alignment: Promotes a natural curve in the spine, preventing undue stress.
- Reduced Wrinkles: Sleeping face-up avoids direct pressure on your face, reducing skin creasing.
- Improved Breathing: This position can be beneficial for people without sleep apnea, as it allows the airways to remain open.
Drawbacks:
- Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Back sleeping can exacerbate snoring and worsen symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Acid Reflux: Gravity may cause stomach acid to travel upward, leading to discomfort.
Tips for Improvement:
- Use a supportive pillow to keep your neck in alignment.
- Consider an adjustable bed or wedge pillow to elevate your upper body and reduce snoring or acid reflux.
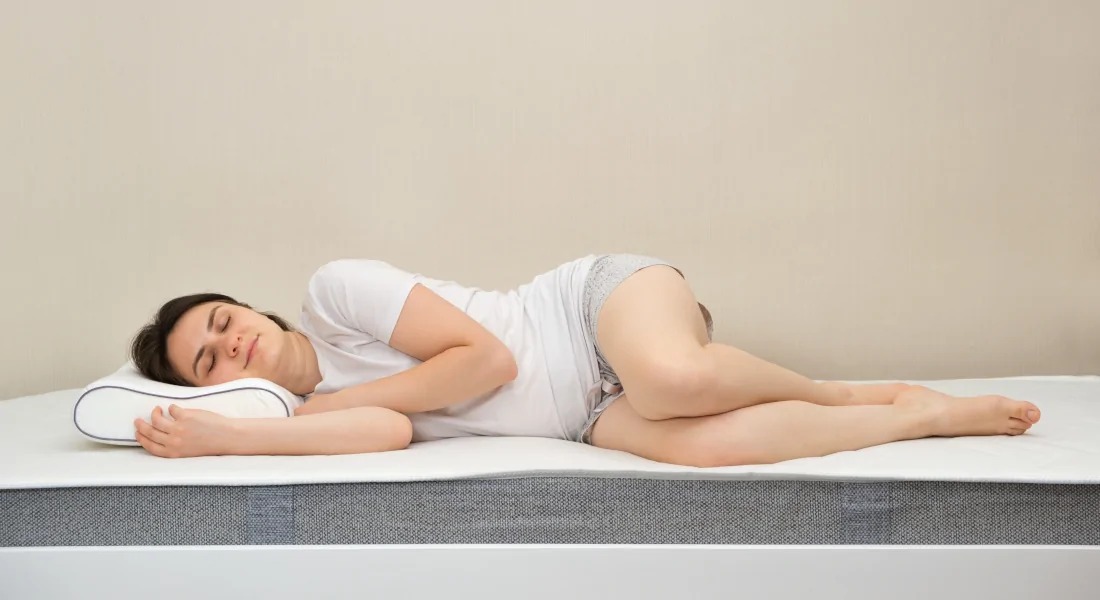
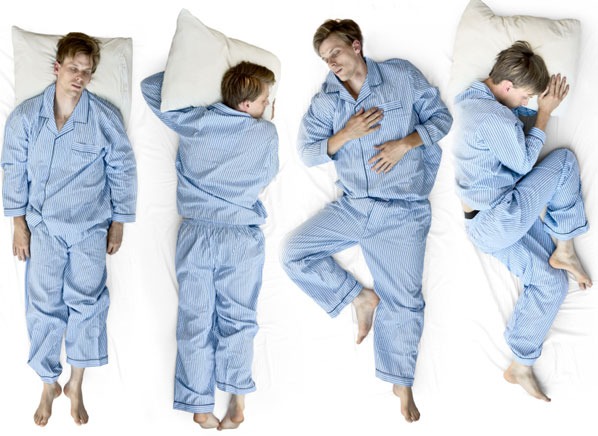
2. Side Sleeping
Side sleeping is the most common position and is highly beneficial for many people. It involves lying on either your left or right side with your legs straight or slightly bent.
Benefits:
- Reduced Snoring: Side sleeping helps keep the airways open, minimizing snoring.
- Better Digestion: Sleeping on the left side can improve digestion and reduce acid reflux by keeping the stomach below the esophagus.
- Pregnancy Comfort: Pregnant individuals are often advised to sleep on their left side to improve blood flow to the fetus.
Drawbacks:
- Shoulder Pain: Prolonged side sleeping can strain the shoulder on which you lie.
- Facial Wrinkles: Side sleeping may increase pressure on one side of the face, potentially leading to wrinkles.
Tips for Improvement:
- Use a firm pillow to fill the gap between your neck and the mattress, keeping your spine aligned.
- Place a pillow between your knees to reduce pressure on your hips and lower back.
3. Stomach Sleeping (Prone Position)
Sleeping on your stomach is often discouraged by sleep experts due to its potential to misalign the spine and strain the neck.
Benefits:
- Reduced Snoring: This position may help reduce snoring for some people by keeping the airways open.
Drawbacks:
- Spinal Strain: The unnatural position of the neck and back can lead to stiffness and pain.
- Facial Pressure: Continuous pressure on the face can contribute to wrinkles and skin irritation.
- Poor Breathing: Lying face-down can make it harder to breathe, leading to shallow respiration.
Tips for Improvement:
- Use a very thin or no pillow to reduce neck strain.
- Try transitioning to a side-sleeping position for better alignment.
Special Considerations for Sleeping Positions

Pregnancy
Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, is recommended during pregnancy. This position enhances blood circulation to the fetus and prevents the uterus from pressing on major blood vessels.
Chronic Pain
For those with back pain, sleeping on the back with a pillow under the knees can relieve pressure on the spine. People with hip pain may benefit from side sleeping with a pillow between the knees.
Sleep Apnea and Snoring
Side sleeping is often recommended for individuals with sleep apnea or chronic snoring, as it helps keep the airways open. Elevating the upper body can also be helpful.
Acid Reflux
Sleeping on the left side can significantly reduce acid reflux symptoms. Raising the head of the bed can further prevent stomach acid from traveling upward.
How to Transition to a Healthier Sleeping Position

Changing your sleeping position can be challenging but not impossible. Here are some tips to help you transition:
- Pillow Placement: Use pillows strategically to support your body in the desired position.
- Gradual Adjustment: Start by spending a small portion of your night in the new position and gradually increase the duration.
- Comfortable Mattress: Invest in a mattress that provides adequate support for your preferred position.
- Body Awareness: Pay attention to how your body feels when you wake up and adjust your posture accordingly.
The Role of Sleep Accessories
Your choice of pillow, mattress, and bedding can significantly impact your sleeping position. Here are some recommendations:
- Pillow: Choose a pillow with the right height and firmness to support your neck and spine.
- Mattress: A medium-firm mattress is generally suitable for most sleeping positions. Side sleepers may prefer a softer mattress, while back sleepers benefit from firmer support.
- Bedding: Opt for breathable and hypoallergenic materials to enhance comfort and prevent allergies.
Conclusion
Your sleeping position plays a pivotal role in your overall health, affecting everything from spinal alignment to digestion and breathing. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, understanding the pros and cons of different positions can help you make informed choices for better sleep.
Whether you’re a back sleeper, side sleeper, or stomach sleeper, small adjustments to your posture and sleep environment can have a significant impact on your well-being. Pay attention to your body, invest in supportive sleep accessories, and consult a healthcare professional if you experience chronic discomfort or sleep issues. By prioritizing your sleeping position, you’re taking an essential step toward improving your health and quality of life.